If you’re reading this post, you’ve been exploring the world of AI and large language models (LLMs)! You’ve probably faced a common dilemma: there are dozens of powerful language models out there—GPT-4, Claude, Llama, and many more—each with their own strengths and specialties. But what if you want to use one model to understand user queries and a completely different one to generate responses? Or what if you need to connect your LLM to your company’s internal documents, databases, or APIs?
Let’s talk about LangChain—an open-source orchestration framework that’s changing how developers build LLM-powered applications.
What is LangChain?
LangChain is essentially a universal adapter for large language models. Launched by Harrison Chase in October 2022, it became GitHub’s fastest-growing open-source project by June 2023—and for good reason. Available in both Python and JavaScript, LangChain provides a centralized development environment where you can build sophisticated AI applications and seamlessly integrate them with data sources and business workflows.
Think of it as the conductor of an orchestra, coordinating different AI models and tools to work together harmoniously.
The Power of Abstractions
At its core, LangChain works through something called abstractions. Let me explain this with a simple analogy: when you adjust your home thermostat, you don’t need to understand the complex circuitry, wiring, or HVAC mechanics behind it. You just set the temperature. That’s an abstraction—a simplified interface that hides complexity.
LangChain does the same thing for AI development. It provides common building blocks that represent the typical steps needed when working with language models, then lets you chain them together to create powerful applications with minimal code.
The Building Blocks of LangChain
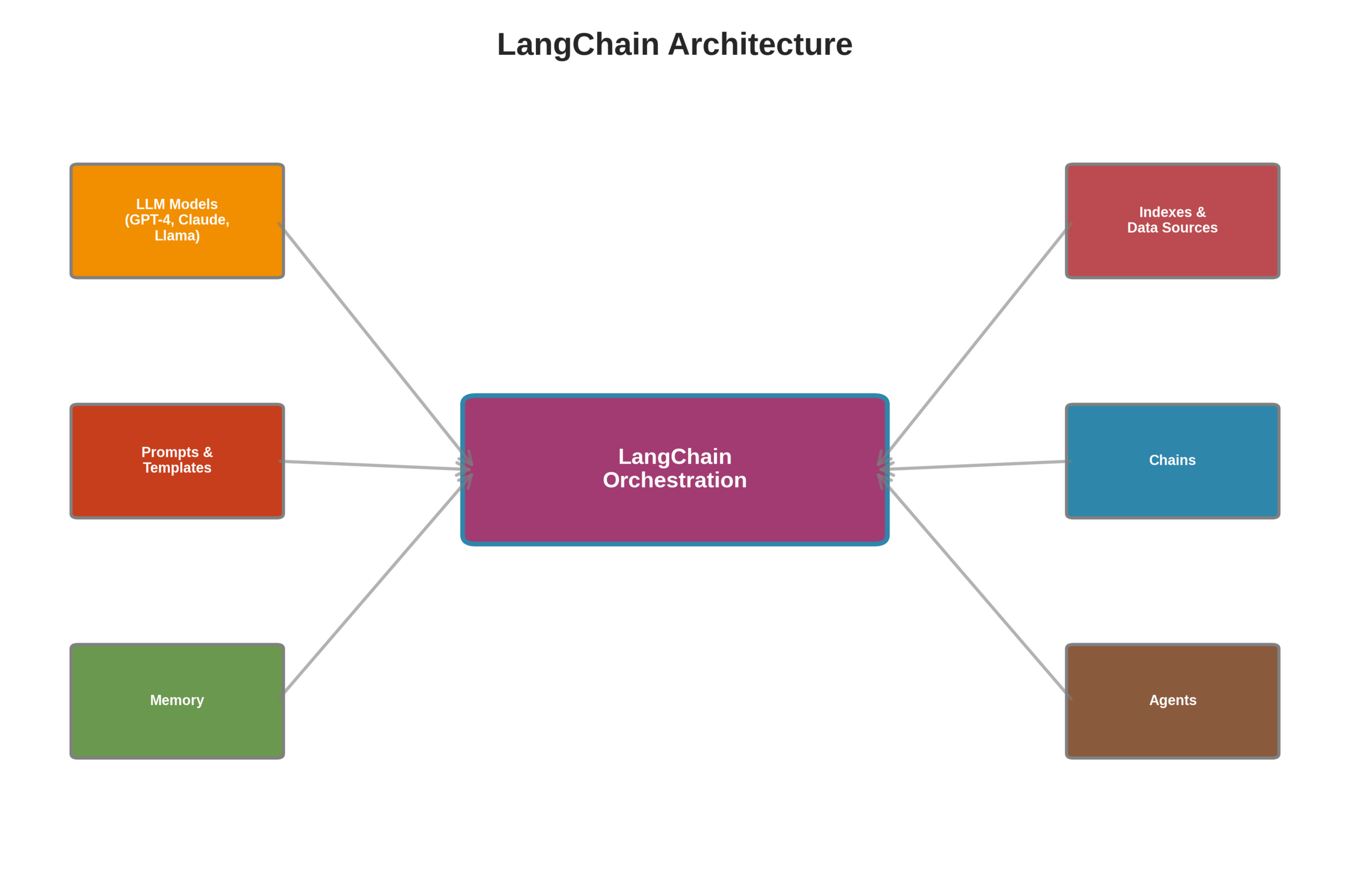 Figure 1: LangChain’s modular architecture showing how different components connect to the central orchestration layer
Figure 1: LangChain’s modular architecture showing how different components connect to the central orchestration layer
Let’s break down the key components that make LangChain so versatile:
1. LLM Module
The beauty of LangChain is its flexibility. You can plug in virtually any LLM—whether it’s a closed-source model like GPT-4 or an open-source one like Llama 2. All you need is an API key. The LLM class provides a standard interface, so you can even use multiple models in the same application, leveraging the best of each.
2. Prompts and Templates
Writing effective prompts can be tedious, especially when you need to include context, instructions, and formatting guidelines repeatedly. LangChain’s prompt template class solves this by formalizing prompt composition. You can create templates that include:
- Specific instructions (“Do not use technical terms in your response”)
- Few-shot examples to guide the model’s behavior
- Output format specifications
This means no more manually hard-coding context into every query.
3. Chains: The Core Workflow
This is where LangChain gets its name. Chains combine LLMs with other components to execute sequences of functions. Imagine building an application that:
- Retrieves data from a website
- Summarizes the content
- Uses that summary to answer user questions
That’s a sequential chain—where the output of one function becomes the input for the next. Each step can use different prompts, parameters, or even different models entirely.
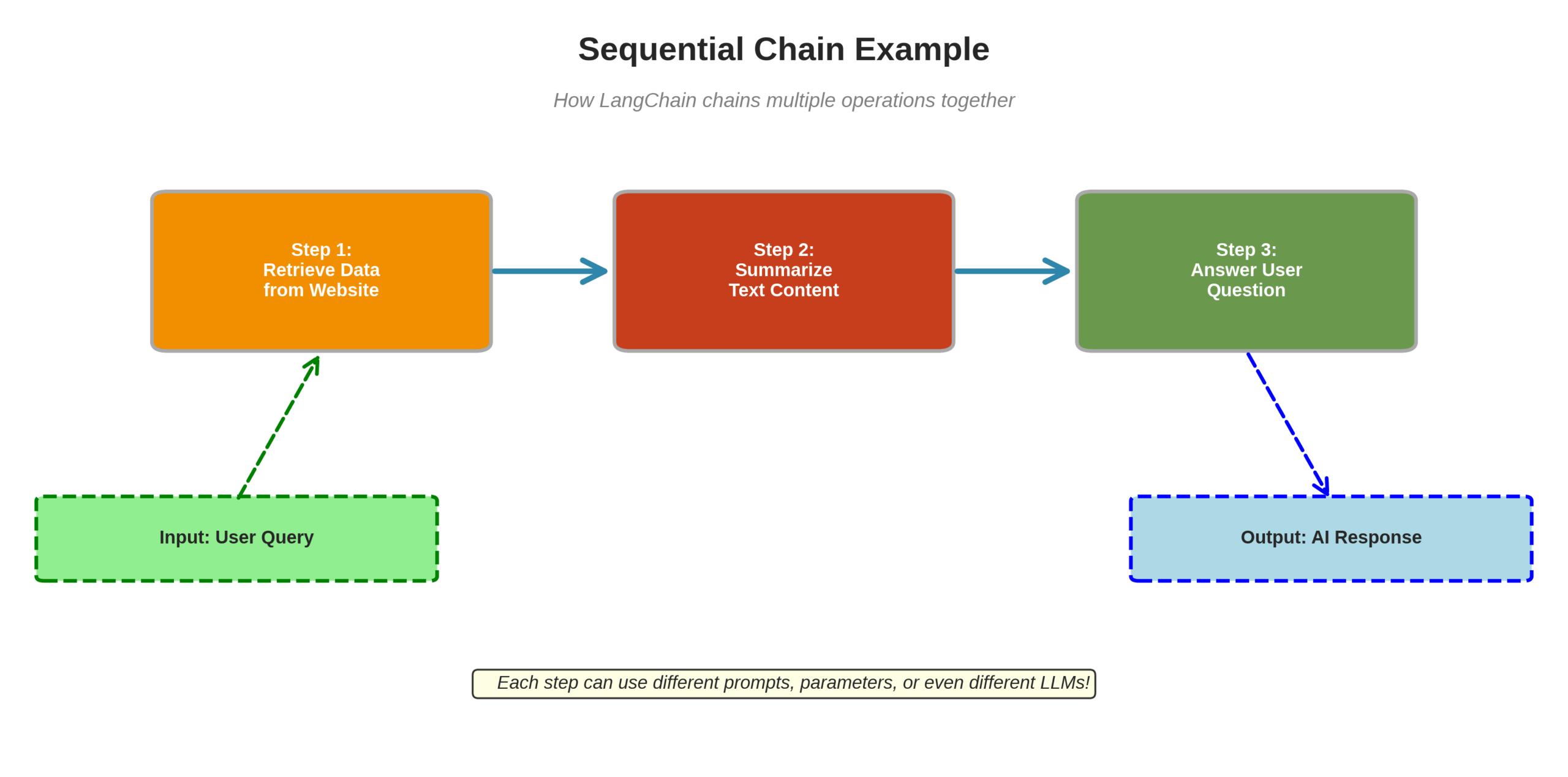 Figure 2: A visual representation of how sequential chains work in LangChain, passing data from one step to the next
Figure 2: A visual representation of how sequential chains work in LangChain, passing data from one step to the next
4. Indexes: Accessing External Data
LLMs are only as good as the data they can access. While they’re trained on vast amounts of information, they don’t know about your internal documents, proprietary databases, or recent events. LangChain addresses this with indexes, which include:
- Document Loaders: Import data from Dropbox, Google Drive, YouTube transcripts, Airtable, MongoDB, and more
- Vector Databases: Store information as vector embeddings—numerical representations that enable efficient retrieval of relevant information
- Text Splitters: Break down large documents into smaller, semantically meaningful chunks that can be processed more effectively
5. Memory: Remembering Context
By default, LLMs don’t remember previous conversations. Every interaction is isolated unless you manually pass chat history as input. LangChain provides simple utilities to add memory to your applications, with options ranging from retaining entire conversation histories to just keeping summarized versions of past interactions.
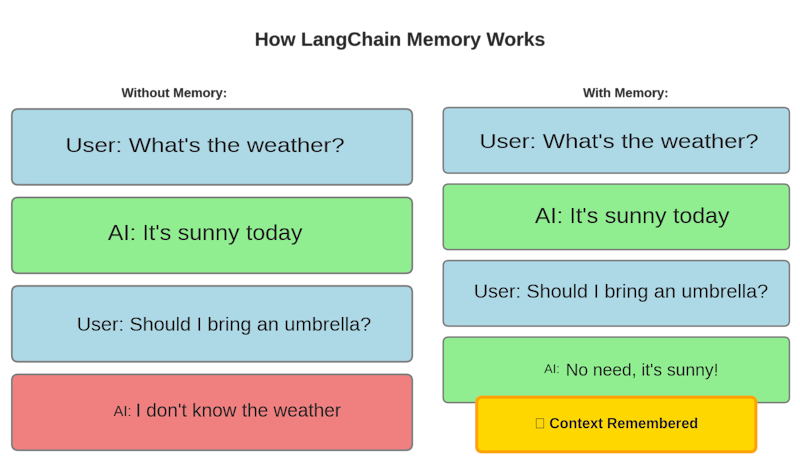 Figure 3: Comparison of LLM behavior without memory vs. with LangChain’s memory system
Figure 3: Comparison of LLM behavior without memory vs. with LangChain’s memory system
6. Agents: Autonomous Decision-Making
Agents take LangChain to the next level. They use a language model as a reasoning engine to determine which actions to take next. When building an agent, you provide:
- A list of available tools
- User inputs (prompts and queries)
- Context from previously executed steps
The agent then autonomously decides how to accomplish its goal, potentially using multiple tools and taking several actions—all powered by RPA (Robotic Process Automation).
Real-World Use Cases
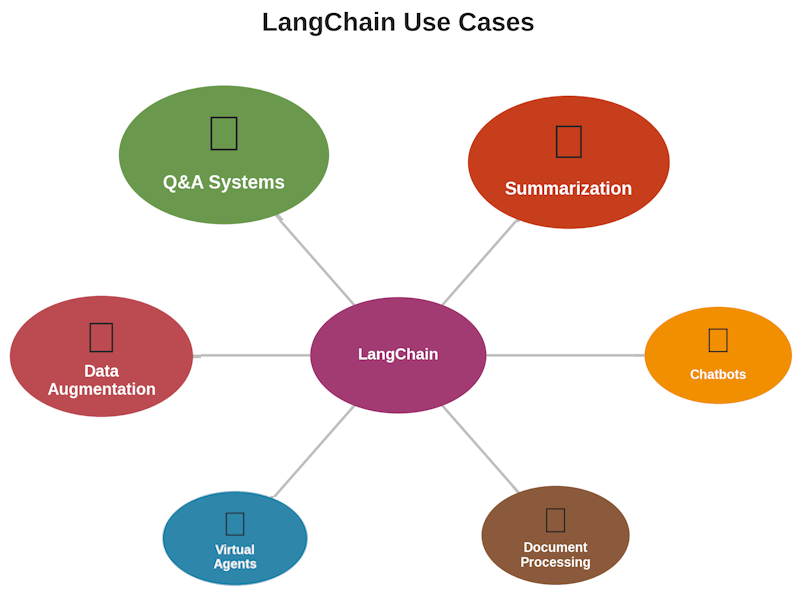 Figure 4: The diverse applications of LangChain across different industries and use cases
Figure 4: The diverse applications of LangChain across different industries and use cases
So how can you actually use LangChain? Here are some practical applications:
Intelligent Chatbots
Build context-aware chatbots that integrate with your existing communication channels and workflows through their APIs. Your chatbot can access company knowledge bases, remember conversation history, and provide relevant, accurate responses.
Document Summarization
Automatically summarize complex academic papers, meeting transcripts, or even your daily email inbox. LangChain makes it easy to process large volumes of text and extract the key information.
Question Answering Systems
Create systems that can answer questions using your specific documents or specialized knowledge bases. The LLM retrieves relevant information from your storage and articulates helpful answers using data that wasn’t in its original training dataset.
Data Augmentation
Generate synthetic training data for machine learning models. LangChain can help create additional samples that closely resemble real data points in your training dataset, improving model performance.
Virtual Agents
Build autonomous agents that can determine their own next steps and take actions to complete tasks—from automating customer service workflows to managing complex business processes.
The LangChain Ecosystem
LangChain isn’t just a single tool—it’s part of a growing ecosystem:
- LangChain (Core): The main framework for building LLM applications
- LangServe: Deploy your chains as REST APIs
- LangSmith: Monitor, evaluate, and debug your applications in production
Best of all? LangChain is entirely open-source and free to use.
Why LangChain Matters
The AI landscape is evolving rapidly, with new models and capabilities emerging constantly. LangChain provides a stable, flexible foundation that lets you:
- Stay model-agnostic: Switch between or combine different LLMs without rewriting your entire application
- Reduce development time: Use pre-built components instead of coding everything from scratch
- Scale efficiently: Build complex workflows that would be difficult to manage otherwise
- Future-proof your applications: Adapt to new models and techniques as they become available
Getting Started
Whether you’re building a simple chatbot or a sophisticated multi-agent system, LangChain’s tools and APIs simplify working with large language models. The framework’s abstractions handle the complexity, letting you focus on building applications that solve real problems.
The future of AI isn’t just about having powerful models—it’s about orchestrating them effectively. And that’s precisely what LangChain enables.
Ready to start building? Check out the LangChain documentation and join the thousands of developers already leveraging this robust framework.
Have you used LangChain in your projects? Share your experiences in the comments below!

